V tomto výučbe sa dozviete, ako funguje Primov algoritmus. Nájdete tiež pracovné príklady Primovho algoritmu v jazykoch C, C ++, Java a Python.
Primov algoritmus je algoritmus s minimálnym rozpätím stromu, ktorý berie ako vstup graf a nachádza podmnožinu hrán tohto grafu, ktorá
- tvoria strom, ktorý obsahuje každý vrchol
- má minimálny súčet váh medzi všetkými stromami, ktoré je možné vytvoriť z grafu
Ako funguje Primov algoritmus
Spadá pod triedu algoritmov nazývaných chamtivé algoritmy, ktoré nachádzajú miestne optimum v nádeji, že nájdu globálne optimum.
Vychádzame z jedného vrcholu a neustále pridávame hrany s najmenšou hmotnosťou, až kým nedosiahneme svoj cieľ.
Kroky na implementáciu Primovho algoritmu sú tieto:
- Inicializujte minimálny spanningový strom náhodne vybraným vrcholom.
- Nájdite všetky hrany, ktoré spájajú strom s novými vrcholmi, nájdite minimum a pridajte ho k stromu
- Opakujte krok 2, až kým nezískame minimálny kostru
Príklad Primovho algoritmu
 Začnite s váženým grafom
Začnite s váženým grafom  Vyberte vrchol
Vyberte vrchol  Vyberte najkratšiu hranu z tohto vrcholu a pridajte ju
Vyberte najkratšiu hranu z tohto vrcholu a pridajte ju  Vyberte najbližší vrchol, ktorý ešte nie je v riešení
Vyberte najbližší vrchol, ktorý ešte nie je v riešení  Vyberte najbližší okraj, ktorý ešte nie je v riešení, ak existuje viac možností, vyberte jednu náhodne
Vyberte najbližší okraj, ktorý ešte nie je v riešení, ak existuje viac možností, vyberte jednu náhodne 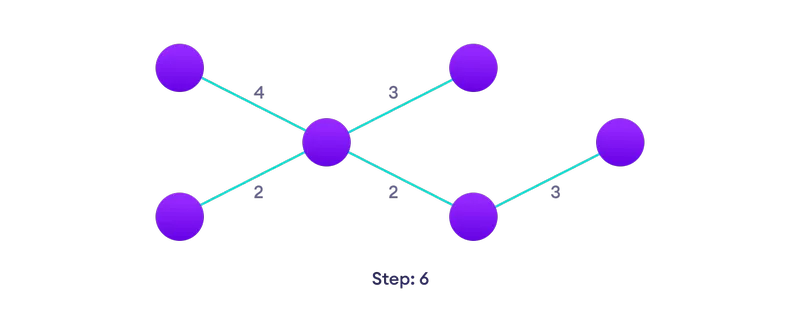 Opakujte, kým mať klenutý strom
Opakujte, kým mať klenutý strom
Primov algoritmus pseudokód
Pseudokód pre primov algoritmus ukazuje, ako vytvoríme dve sady vrcholov U a VU. U obsahuje zoznam vrcholov, ktoré boli navštívené, a VU zoznam vrcholov, ktoré neboli navštívené. Jeden po druhom posúvame vrcholy z množiny VU do množiny U pripojením hrany najmenšej hmotnosti.
T = ∅; U = ( 1 ); while (U ≠ V) let (u, v) be the lowest cost edge such that u ∈ U and v ∈ V - U; T = T ∪ ((u, v)) U = U ∪ (v)
Príklady jazyka Python, Java a C / C ++
Aj keď sa používa grafická reprezentácia susednej matice, tento algoritmus je možné na zvýšenie efektívnosti implementovať aj pomocou služby Adjacency List.
Python Java C C ++ # Prim's Algorithm in Python INF = 9999999 # number of vertices in graph V = 5 # create a 2d array of size 5x5 # for adjacency matrix to represent graph G = ((0, 9, 75, 0, 0), (9, 0, 95, 19, 42), (75, 95, 0, 51, 66), (0, 19, 51, 0, 31), (0, 42, 66, 31, 0)) # create a array to track selected vertex # selected will become true otherwise false selected = (0, 0, 0, 0, 0) # set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0 # the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be # always less than(V - 1), where V is number of vertices in # graph # choose 0th vertex and make it true selected(0) = True # print for edge and weight print("Edge : Weight") while (no_edge G(i)(j): minimum = G(i)(j) x = i y = j print(str(x) + "-" + str(y) + ":" + str(G(x)(y))) selected(y) = True no_edge += 1
// Prim's Algorithm in Java import java.util.Arrays; class PGraph ( public void Prim(int G()(), int V) ( int INF = 9999999; int no_edge; // number of edge // create a array to track selected vertex // selected will become true otherwise false boolean() selected = new boolean(V); // set selected false initially Arrays.fill(selected, false); // set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0; // the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be // always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in // graph // choose 0th vertex and make it true selected(0) = true; // print for edge and weight System.out.println("Edge : Weight"); while (no_edge < V - 1) ( // For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices // , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1. // if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise // choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1. int min = INF; int x = 0; // row number int y = 0; // col number for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) ( if (selected(i) == true) ( for (int j = 0; j G(i)(j)) ( min = G(i)(j); x = i; y = j; ) ) ) ) ) System.out.println(x + " - " + y + " : " + G(x)(y)); selected(y) = true; no_edge++; ) ) public static void main(String() args) ( PGraph g = new PGraph(); // number of vertices in grapj int V = 5; // create a 2d array of size 5x5 // for adjacency matrix to represent graph int()() G = ( ( 0, 9, 75, 0, 0 ), ( 9, 0, 95, 19, 42 ), ( 75, 95, 0, 51, 66 ), ( 0, 19, 51, 0, 31 ), ( 0, 42, 66, 31, 0 ) ); g.Prim(G, V); ) )
// Prim's Algorithm in C #include #include #define INF 9999999 // number of vertices in graph #define V 5 // create a 2d array of size 5x5 //for adjacency matrix to represent graph int G(V)(V) = ( (0, 9, 75, 0, 0), (9, 0, 95, 19, 42), (75, 95, 0, 51, 66), (0, 19, 51, 0, 31), (0, 42, 66, 31, 0)); int main() ( int no_edge; // number of edge // create a array to track selected vertex // selected will become true otherwise false int selected(V); // set selected false initially memset(selected, false, sizeof(selected)); // set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0; // the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be // always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in //graph // choose 0th vertex and make it true selected(0) = true; int x; // row number int y; // col number // print for edge and weight printf("Edge : Weight"); while (no_edge < V - 1) ( //For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices // , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1. // if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise //choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1. int min = INF; x = 0; y = 0; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) ( if (selected(i)) ( for (int j = 0; j G(i)(j)) ( min = G(i)(j); x = i; y = j; ) ) ) ) ) printf("%d - %d : %d", x, y, G(x)(y)); selected(y) = true; no_edge++; ) return 0; )
// Prim's Algorithm in C++ #include #include using namespace std; #define INF 9999999 // number of vertices in grapj #define V 5 // create a 2d array of size 5x5 //for adjacency matrix to represent graph int G(V)(V) = ( (0, 9, 75, 0, 0), (9, 0, 95, 19, 42), (75, 95, 0, 51, 66), (0, 19, 51, 0, 31), (0, 42, 66, 31, 0)); int main() ( int no_edge; // number of edge // create a array to track selected vertex // selected will become true otherwise false int selected(V); // set selected false initially memset(selected, false, sizeof(selected)); // set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0; // the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be // always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in //graph // choose 0th vertex and make it true selected(0) = true; int x; // row number int y; // col number // print for edge and weight cout << "Edge" << " : " << "Weight"; cout << endl; while (no_edge < V - 1) ( //For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices // , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1. // if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise //choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1. int min = INF; x = 0; y = 0; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) ( if (selected(i)) ( for (int j = 0; j G(i)(j)) ( min = G(i)(j); x = i; y = j; ) ) ) ) ) cout << x << " - " << y << " : " << G(x)(y); cout << endl; selected(y) = true; no_edge++; ) return 0; )
Primov vs Kruskalov algoritmus
Kruskalov algoritmus je ďalší populárny algoritmus minimálneho rozpätia stromu, ktorý používa inú logiku na vyhľadanie MST grafu. Namiesto toho, aby Kruskalov algoritmus vychádzal z vrcholu, triedi všetky hrany od nízkej po vysoké a neustále pridáva najnižšie hrany, pričom ignoruje hrany, ktoré vytvárajú cyklus.
Zložitosť Primovho algoritmu
Časová zložitosť Primovho algoritmu je O(E log V).
Aplikácia Primovho algoritmu
- Kladenie káblov elektrického vedenia
- V sieti navrhnuté
- Vytvárať protokoly v sieťových cykloch








